The first mobile phones were commercially introduced in the 1980s when they were used in specific locations like cars, remote offices, or building sites. Since then we have witnessed a significant sophistication in interaction practices, to the extent we hardly find any business person who does not carry a mobile.
From the touring CEO to an engineer working in the field, mobility solutions have drastically changed the way people work. On the other hand, mobile technologies too have matured in terms of their capabilities which are approaching personal computer-like features such as supporting email, web access, etc.
Today mobility moves far beyond the communication, the technological advancements in microchips and sensor technologies that are used to track vehicles, objects, and humans, like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Near Field Communication (NFC), and the Global Positioning System (GPS) serve a wide range of purposes for business.
Enterprises are grappling with ways enterprise mobility has to offer.
What exactly is Enterprise Mobility?
Enterprise Mobility is the new channel that disseminates information, facilitates communication, and allows the workforce to do their jobs from a variety of mobile devices like smartphones, HHDs, tablets, personal digital assistants, laptops, etc.
Such mobile devices can perform, support, accomplish, coordinate and manage the work activities and organizational tasks to enable the right information at right time to enhance transactions and collaboration outside workplaces & times.
Evolution of Enterprise Mobility(EM)- Unfolding Advancement
Even though the mobile phone was first introduced by AT&T in 1946, the enterprise mobility segment actually started in 1991, when ‘Hermes’– a system management server (SMS) was released by Microsoft.
With the proliferation of personal computers, a unified solution to manage these devices became essential. A big change happened when the digital Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) was introduced for voice telephony.
The use cases of mobile devices changed dramatically with the introduction of GSM.
During the 90s and the last decade, Desktop management solutions witnessed an increased adoption. Also, with the workforce bringing personal digital assistants and mobile phones to the workplace, they wanted to have the flexibility to access emails, calendars, contacting, and the other work.
This change presented varying degrees of security and created a nightmare for the IT staff to manage. This emphasized the need for Mobile Device Management (MDM) to ensure the functionalities are optimized and the devices are safe and at the same time assuring that the corporate network is protected.
The first version of Exchange Active Sync (EAS), a part of Mobile Information Server (MIS) 2002, was developed to manage emails and contacts that required a power-on password to access corporate e-mail.
Later several versions of the protocol were developed to introduce new policies. Since then EAS was the most common mobile device management and protocol control solution used commercially.
Later the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) trend was born. Employers soon started adopting BYOD policies and took their enterprise mobility initiatives a step forward. Soon in 2016, IT professionals listed down the top benefit of enterprise mobility as productivity.
As a result, several other trends like Choose Your Own Device (CYOD) and Corporate Owner Personally Enabled (COPE) evolved.

Why Enterprise Mobility Solutions?
There are multi-fold reasons why enterprise mobility should be embraced by organizations. The recent pandemic has well highlighted the importance of enterprise mobility and how it helped to survive the business world during an unseen crisis.
Not just sales or field support applications, but it supports value-added service (VAS) and cross-functional activities that help organizations to respond speedily to customer delight.
Enterprise mobility is the graceful use of technology that helps to increase the work-life balance & retain young employees.
Some of the reasons to proactively adopt enterprise mobility at your organization are:
- Employee Productivity: Enterprise mobility empowers employees with the tools & data that are readily available on their mobiles. This reduces the turn-around time and improves the productivity of the employees. A Forrester study reveals that 75% of companies reported an increase in worker productivity post-deployment of mobile apps.
- Reduce Costs & Time: EM facilitates communication between various stakeholders. Usually, with administrative support this can be made seamless; however, it incurs a huge cost and time. EM with its self-service capabilities allows these remote users to manage performance, communicate, etc which slashes administrative costs & time and increase employee job satisfaction.
- Communication: In organizational siloes, frequent friction is seen between various processes. Enterprise mobility by establishing real-time communication between workflow management systems and mobile devices can remove this friction and facilitate seamless communication that results in reduced delays in task execution, approval, review, or action.
- Accountability: EM along with real-time communication allows real-time monitoring that coerces organizations to focus on best practices. It enables a greater insight & visibility into an organization’s resources and assets, to create an instrumented enterprise that has accountability at all levels. Mobility solutions infused with wireless sensor technologies & RFIDs can rapidly detect or pre-empt failures much before they occur.
- Scalability: Enterprise mobility solutions allow to integrate the legacy systems to cloud platforms. This not only enhances the value of business models but also improves their independence and scalability. Cloud platforms ensure that future business needs are accommodated and the resources or data are accessible on the go at any time anyplace.
- Data Collection: Mobility solutions offer multiple touch points, the data collected at such touch points can offer valuable & meaningful insights to the business. Business intelligence is crucial for organizations to analyze and adapt to changing user needs. Mobility solutions can facilitate data collection seamlessly and provide organizations with much-needed insights.
- Competitive Advantage: Strategic implementation of enterprise mobility can lead to a competitive advantage for the organization. It can revamp the core competencies that can change organizational business models and strategies. It’s noteworthy that the mere adoption of enterprise mobility solutions does not guarantee a business value. There needs to be a charted strategy to implement mobility in the right functions and processes and is made available to the right set of users to drive the greatest value.
- Business Value: Business value is often considered when making any investment decision. The ability to access the network and resources anytime and anywhere is clearly the reason why enterprise mobility is essential to adopt. By replacing expensive computing equipment with tiny, portable, and inexpensive handheld devices the employees can immediately connect with all resources, and reduce errors to drive business efficiency of employees, processes, and resources.
The convenience, efficiency, decision speed, productivity, and process improvement it supports are cited as near-term reasons to adopt enterprise mobility.
In the long-term, EM can fundamentally transform business, create new competitive advantages and redefine the core competencies to influence entire business models, strategies, markets, and industries.
Its overarching benefits in terms of strategy, transaction information, enterprise transformation & business value answer the question of why enterprise mobility.
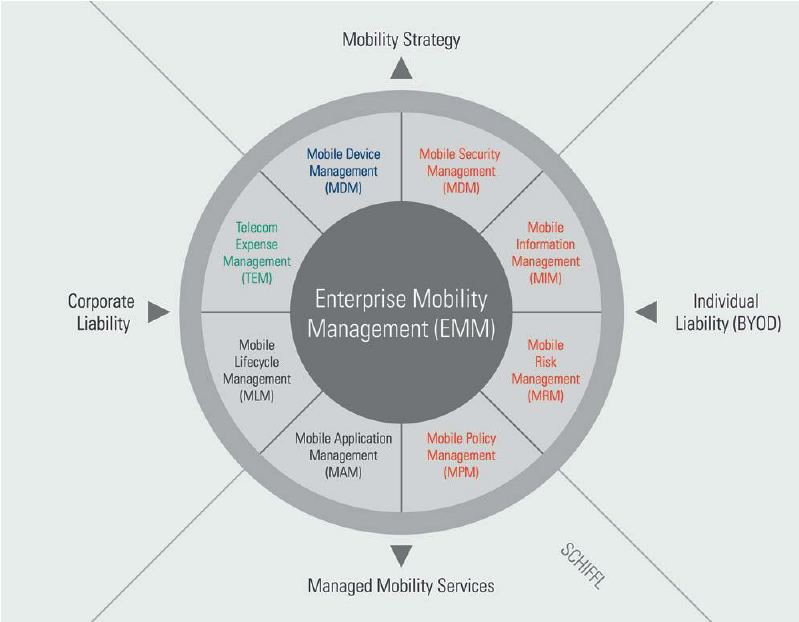
EMM (Enterprise Mobility Management)- What’s Under the Hood?
The increasing array of mobile devices & services in a business context necessitates the need for efficient mobility management. Enterprise mobility management (EMM) is the set of tools, people, processes, policies, and technologies to manage and support the broad mobile device use in an organization.
Such systems are termed Enterprise Mobility Management Systems (EMMS). EMMS is an end-point-independent mobile solution that enables an organization to support & manage service levels irrespective of the devices they use.
Key components of Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM)- Mobility at Work
The EMM is composed of three main components:
- Mobile Device Management (MDM)– Control the devices
- Mobile Application Management (MAM)– Control the access
- Mobile Content Management (MCM)/Mobile Information Management (MIM)- Limited access to data
Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM operates on a device level wherein monitoring, controlling, and ensuring the security of the application registered on various mobile platforms in an insecure network is administered by an admin.
Despite additional costs, it is crucial to ensure data security and accountability. With the rising BYOD culture, the vulnerability to security threats increases, and MDM ensures device security with its robust architecture and four main components- MDM Server, Management Console, Relay Server, and Mobile Agent.
Mobile Application Management (MAM): MAM is responsible for distributing and publishing mobile apps and services to various devices within an organization. It controls the access by monitoring which user can download which app. It enforces the policies on how to access particular internal apps and services.
MAM consists of two main components- Publisher and App Store. Publisher ensures which console or mobile apps are uploaded & published on the enterprise app store, whereas, from the app store the apps can be accessed and installed by specific users.
Mobile Information management (MIM): MIM/MCM allows approved apps or devices only to access the organization’s sensitive data and resources by filtering the users.
It ensures device-agnostic security that keeps crucial data in an isolated container that is encrypted and only authenticated users can access and transmit it.
Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) at Work
Traditionally, mobility solutions were simple trans-coded applications of existing corporate data that used mobile devices; however, the concept of mobility evolved over time. Today, it takes contexts like users, tasks, devices, and uses into consideration.
The Top EMM Applications in an Organization are:
Device and information management
EMM enables mobile devices to access key corporate assets with ensuring compliance, it can enforce advanced security settings. Based on the user, device, & OS, it can provide policy options and restrictions.
Mobilization of e-mail, personal information management (PIM) tools like calendars, contacts, schedule management, and enterprise portals is one of the fastest-growing enterprise mobility applications. EMM enforces policies and advanced rules for access control based on groups, device compliance, and device attributes.
App Protection & Distribution
Now-a days enterprise apps are often containerized using technologies that do not require source code changes, EMM can add a security layer & policy management around an app without changing source code or embedding SDK.
With EMM, app developers do not need to worry about app security, app protection policies like secure app connectivity, user authentication, access, data encryption, document sharing, copy/paste, etc can ensure app security and prevent them from going to unauthorized sites.
The EMM suite also ensures easy distribution of apps by allowing only authorized users to access with corporate security & data protection. Whenever an employee leaves or a device is no longer in use, it revokes apps and data securely.
Authentication
EMM can enforce robust authentication methods and support requirements on email, VPN, Wi-Fi, Symantec Managed PKI Service integration, and Microsoft Certificate Authorities. No matter if it is a third party, cloud, or an in-house enterprise app, EMM can provide single sign-on functionalities by using highly responsive authentication methods like LDAP, SiteMinder, and SAML.
Threat Protection
Malicious threats and unauthorized access to sensitive organizational data are difficult to protect. EMM utilizes modern protection tools like web browser protection & antimalware to protect the devices and meet compliance requirements.
EMM can also protect the device with anti-theft protection wherein administrators can locate, lock, and wipe the device data as required. It can further ensure protection against a threat with the capabilities to blacklist and whitelist the users.
Content Distribution
In another application, EMM can help corporates in distributing content to end-users. Admins can distribute documents and multimedia content, that have different file formats securely. It can apply appropriate corporate security policies at a per-file level. The EMM suite can support content update and revocation seamlessly.

Things To Know Before Choosing an EMM Service Partner
The leading EMM vendors are Microsoft, Jamf Pro, VMware, Blackberry, etc that provides a suite of services like mobile security, device management, application management, content management, email management, information and expense management, web browser security, BYOD, & multi-user management.
Other emerging enterprise mobility management solution providers like Fusion Informatics Limited are offering innovative solutions that provide the full suite of required features and functionality that can be deployed, managed, and maintained either on-premise or cloud.
Each EMM product has its own functionality and set of features; however, not all features are supported by your mobile platforms, a smaller product with specific functionalities and business requirements that are customized as per business needs is good to go for SMEs.
While selecting an EMM service provider there are certain aspects that need to be considered:
- Deployment- Cloud or on-premise.
- Implementation- Installation or custom programs
- Hardware- Best-in-class or own
- Security- Configurable or preconfigured
- Architecture- Open, extensible, multi-tenant, or change-ready
- Network- Preconfigured or configuration required
- Integration- With enterprise systems or APIs
- Upgrades- Automatic or manual
- Migrations- on-premise or cloud
- Licensing– Per-user or per-device
No matter where your business data and information live, an ideal enterprise mobility management product should provide a data access experience that users will embrace, respect & enforce granular policy controls, ensure end-to-end security, does not disrupt the existing business processes, enables simple & efficient team collaboration tools and is highly flexible & storage-agnostic.



