In the hyperconnected world, organizations are embracing a range of new ideas into their structure and have turned towards Business Process Automation (BPA) as a way to enable flexibility, efficiency, and responsiveness within the organizations. It is, therefore, not surprising the impact of BPA is wide-ranging and its introduction in the business has both managerial and technical ramifications.
What is a business process?
Business processes are a set of tasks or activities that must be executed in a certain sequence to achieve the desired business goal. It is the backbone of any organization and even a minor error can cause significant loss. It is essential for companies to pay constant attention to the improvement of these processes in order to pursue operational & process excellence.
Business Process Automation is a fundamental change in the way organizational activities are organized and executed by using a broad range of technologies. It supports the specific work activities and automates the tasks that were previously performed by humans
. The work is delivered to the resources that can either be human or software applications when it needs to be executed. The specification may consist of fetching highly complex dependencies between tasks and other resourcing strategies, which makes the entire process complex. Automation engineering has a central role to play here.
Business Process Automation ensures that all the assets continuously operate predictably within the most profitable range to drive consistency, reliability, better yield, and improved quality using minimal energy.
In a large corporation, business processes span across various departments and stakeholders. Manual and undocumented processes are cumbersome to control & visualize and the situation becomes even more complex in the case of organizations that are distributed geographically. It raises a risk of stakeholders using outdated or inaccurate information to create the possibilities for guesswork and frequent improvisation.
Through automation, repeatable, enforceable, and managed processes can be developed. Business process automation can be used to improve visibility in processes with real-time status and reporting.
Business process automation leverage a broad range of technologies and is often covered under popular enterprise apps like ERP, HRMS, and other tools that enforce the best practices in the industry. Some of the common types of business process automation are:
- Basic Automation: Simple, rudimentary tasks are automated to eliminate errors and improve transactional work. The most common examples are Business Process Management and Robotic Process Automation.
- Process Automation: In order to manage the business processes consistently and drive transparency, process automation is leveraged. It can significantly improve productivity and efficiency along with providing valuable insights.
- Advanced Automation: Advanced automation integrates multiple systems to support complex processes. It relies on unstructured data powered by machine learning, NLP, and predictive analytics.
- Intelligent Automation: Intelligent automation harness the power of AI to automate tasks. The system can learn and make decisions based on the situations they have experienced and analyzed.
Business Process Automation is based on three basic principles:
Regardless of the scope, scalability, and complexity of the system, BPA is based on the interlinking of three critical pillars- Orchestration, Integration, and Dynamic Process Automation. Orchestration empowers managers and the IT team to collaborate & automate the processes with the help of visually appealing interfaces.
The integration enables the communication between systems & applications to implement critical process flows that can facilitate decision making. The final pillar is dynamic process automation, wherein rule-based and automatic execution is facilitated amongst various systems to streamline the processes and eliminate errors from manual tasks.
Why Should you Automate Business Processes?
Ask your employees about their least favorite tasks at their job, and the most probable answer is a lot of paperwork & documentation that is repetitive, and tedious. Such tasks take away significant man-hours without adding value to their lives. Apart from process improvement, automation help to free up the knowledge workers for more strategic and creative tasks.
Humans are not the best when it comes to remembering and repeating things, machines are. An organization can improve the potential of its employees by automating the mundane processes using technology. Business process automation offers numerous benefits, which is why businesses are turning their attention toward integrating automated processes in their business management system with the aim to either save or make money.
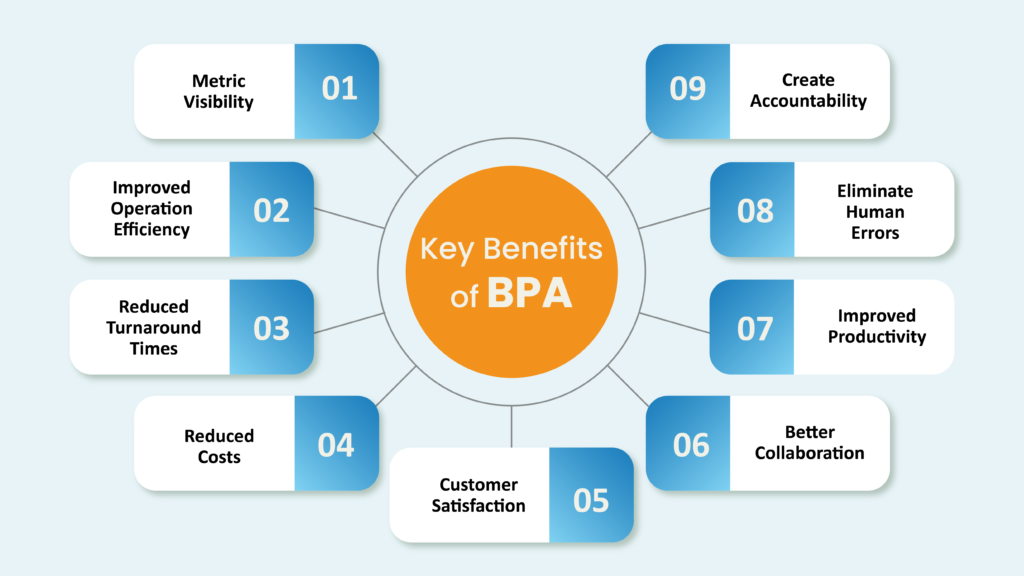
Here are a few reasons why you should automate your business processes:
Business Agility
The business is changing faster than ever. According to the ‘Survival of the Fittest’ theory, changing quickly is an essential trait to ensure sustainability or one has to see itself be overtaken by competitors.
Organizations are becoming highly demanding as to how often & quickly they need changes. This pressurizes the IT team that is already overworked & has a limited budget. Business process automation can help by offloading some work of IT and letting the employees focus on tasks that add more value.
A business can be agile by establishing a system that allows its decision-makers to react rapidly to changes with minimal disruption. Automation can prepare an organization to be fully prepared to adapt and remain flexible for long-term success.
Visibility
One of the reasons why your business should automate is the need for end-to-end visibility. The key to improving performance with a high degree of reliability is automation. If your business has processes that span multiple vertical systems across departments and each of which may have various workflows and reporting built-in, the struggle persists to get full end-to-end visibility.
When a business process is automated, the maximum value an organization garners out of it is understanding the process in-depth and further optimizing it based on the knowledge gained. While implementing business process automation, the issues can be identified and improved before they become big.
Compliance
The ever-changing government rules and regulations are difficult to comply with. To add further to the complexities, the organizations that need to comply with multi-country regulations incurs significant cost and efforts related to regulations. Even though compliance is not a competitive area for business, & all organizations in the industry have to comply with the same set of rules. Compliance is an essential area to focus on as it may lead to a serious negative effect on business.
Automation can increase the traceability as to who has changed the process & review the historical process data, along with enabling orchestration of the best practices that reduce the risk of breaching the compliance.
Employee Efficiency
Every employee has their own thought process and decision-making, which means the process isn’t consistent & predictable. This leads to increased risk and less efficiency. Automation can ensure a well-designed routing, and parallel work to ensure high employee efficiency. It can defuse the conventional siloes, where employees need to wait by facilitating communication between teams, departments, and multiple sites.
Business process automation can help achieve smarter workflows that are unified with the processes, increase system uptime, reduce scrap & rework and enable real-time monitoring & tracking at every stage to improve the efficiency of employees and save their valuable time.
Customer Experience
A significant improvement in processes can be witnessed by modeling them and then executing them in a unified system. Automation can help drive commonality in the processes across an organization. It ensures the process is handled in the same way every time to ensure the same experience is provided to customers, partners, and employees.
Using technologies like AI, ML & NLP, highly responsive customer support can be offered by tracking the customer’s actions and understanding their needs.
Automation can help identify the customer issues, and their intent to provide real-time support. Increased customer satisfaction and retention are the certain benefits of business process automation.
Business Process Automation Examples
Automation experts often opine how automation brings about higher productivity, saves time, and frees employees for more creative tasks. The most common belief is automation greatly helps data management and record-keeping; however, it enables absolute control over various business processes within and between organizations. The six classes of business processes that automation revolutionalize the most are:
Accounting Processes:
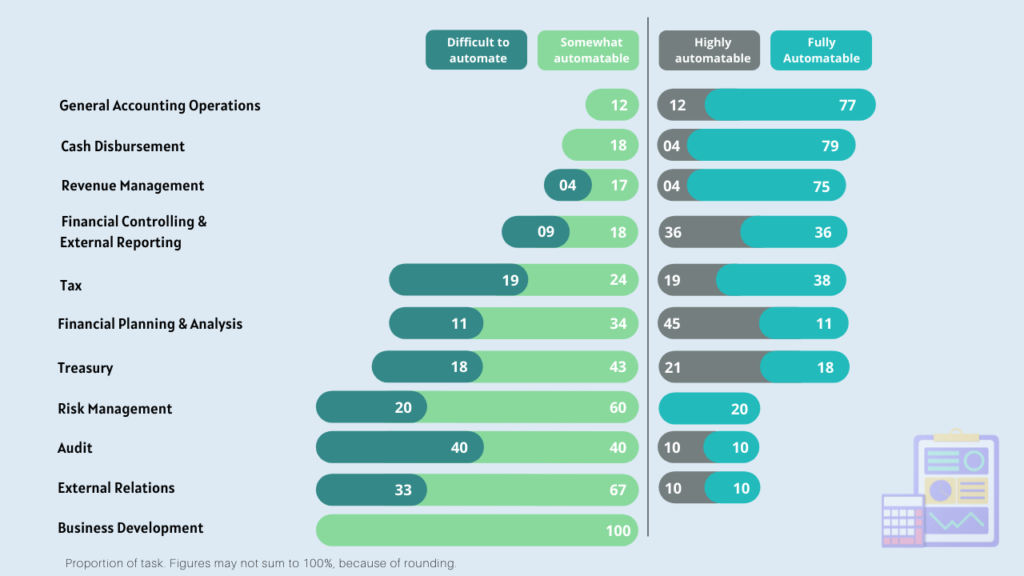
The various financial & accounting processes that can be automated are account payable & receivable clearance, financial closures, supplier management, general accounting, cash disbursement, financial control & reporting, revenue management, tax, financial planning & analysis, risk management, etc.
Administrative Processes
Administrative support processes like time-keeping, mailroom, leave applications, library services, calendar syncing of multiple people, appointment scheduling, statement of work, customer database, bills payment, etc are some of the tasks that can be automated to take away the mundane missions of the day. It will take routine and repetitive tasks off the list to focus on important ones and increase productivity.
Core Processes
Value-added services that directly impact customer satisfaction and their needs and are strategically crucial for an organization like order entry, claims processing, design engineering, employee onboarding, customer relationship management, workflow assignment, task management, chatbots, etc are the most celebrated examples of automation.
Customers are usually at the beginning and end of core processes and their wishes & fulfillment are critical for business success, which is why automating such processes can ensure consistency and resilience in the organization.
Management Processes
Business processes that support management planning & control functions like planning, budgeting, and performance reporting are also common examples of business process automation. Automation can assist management processes that assist planning, organizing, staffing, directing & coordinating. A considerable amount of time can be spared.
Ad hoc Processes
Business processes that satisfy unique and transient needs are ad hoc that are usually undocumented or unmonitored. They create chaos and are unpredictable. Automation of such processes enables visibility in organizational operations, brings stability to processes, and helps the organization stay competitive. Examples are processes that support special staff meetings, promotions, small projects, conferences, etc.
Knowledge-Intensive Processes
Knowledge-intensive processes that gather and process information or knowledge that emphasize the core competence of the organization require very specific knowledge. Typically expert involvement is critical to driving the success of such processes; however, parts of the process could be supported by automation. Examples can be a new product or service development, marketing processes automation, software development & strategy development, etc.
Automation in Action…..
Some of the most common examples of business process automation in business today are:
Chatbots
AI-driven bot automation solutions are the communication channel that had witnessed the largest growth with 92% since 2019 (Drift). Users engage with chatbots in a variety of ways like purchases, meeting scheduling, inquiry, sign-ups, ticket booking, etc, making an efficient self-service tool for users. Chatbots help reduce the costs and time of support.
Employee Onboarding & Offboarding
Automated employee onboarding and offboarding processes leave a lasting imprint on the employees and speak about the company’s culture. On the other hand, it can navigate the business challenges like lack of resources, unstandardized processes, legal compliances, employee turnover, etc.
Automation of employee onboarding tasks like document distribution, & authorization, secure IT provisioning, pushing benefit plans, etc, and offboarding tasks like access removal, scheduling exit interviews, farewell email, gift, etc can create an amicable welcome and goodbye to the employees.
Customer Onboarding
Seamless customer onboarding is critical for long-term customer satisfaction. Automation of customer onboarding activities like workflow digitalization & system integration, touchpoints management, form automation, contracts & proposal automation, quotes & invoice management, etc, can drive highly productive results. A consistent customer onboarding impact customer retention rate and ultimately the business outcomes.
Accounts Payable
Tedious manual data entry and repetitive validations in the accounts payable process involve high chances of errors and are time-consuming. Automation of invoicing, AP workflows, data entry, matching & verification can significantly prevent fraud and increase transparency in the system.
Task Scheduling
Task scheduling tools can manage and automate the tasks effortlessly along with eliminating the need to switch between various applications. Scheduled task automation executes at the designated time even when the system is off, this saves extensive time and provides a comprehensive view of the overall tasks to increase productivity and ensure the optimized use of resources.
How to start your business process automation journey?
The business process automation journey varies for every organization; however, there are some universal steps to get started. To realize the full potential of BPA, a phased approach is essential. Many organizations have experienced success by focusing on developing awareness and adoption across the organization along with building capabilities and skills.
The automation maturity model can progress across three phases- Initiation, Industrialization, and Institutionalization. Here let’s focus on the Initiation phase which emphasizes establishing the capabilities of the organization.

- Product & Process Evaluation
During this step, it is required to evaluate the products and identify the candidate processes to automate. This is possible by understanding the difference between the capabilities of humans and machines. Humans are less capable when it comes to repetitive and mundane tasks; however, machines are very good at it.
Identifying the processes that are best done by humans and machines can help identify the candidate processes to automate. Further, a business case can be created based on the analysis if it makes sense to automate the process.
- Project Mobilization
Once the process that can be automated is defined and the business case is created, it is essential to get it approved. At this stage, the resources required to automate the process can be determined and secured to mobilize the project further. The organizational roles can be defined along with the broader changes that are essential to support automation.
- Design & Development
Roll out standardized design, processes, & approaches to define the scope and benefits extended by automation opportunities. Further, the outcomes against KPIs can help build an awareness of automation throughout the organization. Getting input from the employees who are directly affected makes sense to design & develop the workflows. Training the core team and establishing the environment, architecture, and delivery methodology can support the initial processes.
- Launch
During the launch phase, few processes can be automated using the right tools identified in the previous stage. Automation can either be a success or fail, testing the process efficiency can help understand the gaps and optimize the automation further.
- Ramp-up
The next processes identified in the first stage can be automated. If required advanced training can be given to the affected employees. Measuring automation benefits and effectiveness can help tweak the process and ensure volume ramp-up.
- Continuous Improvement
Automation is a continuous process, to make it run smoothly with minimal or no human intervention, continuous improvement is essential. The best practice is to review and automate regularly to assess what improvements are required to make it more impactful. Continuous improvement is the constant pursuit of perfection in all efforts.
What Is the Goal of Process Automation?
While flexibility, reliability, transparency, performance, and scalability are often sought as the goal of process automation, it aims to create a common enterprise-wide view of each business function and is considered the form of doing business that spurs the organizational growth and transformation. Some of the top goals for implementation of the automation techniques as a part of a business process are:
Transaction Frequency & Repeatability:
Process automation enables a simple, integrated, streamlined process flow that frees human capital from mundane tasks. The monotony of the work reduces the productivity at the workplace as there are fewer chances of achieving the same results when a repetitive task is done by humans, therefore, an automation’s primary goal is to increase the business outcomes by automating high frequency and repetitive tasks. By coordinating tasks and routing them efficiently, automation improves business processes manifolds.
Operational Excellence:
Reaching a new level of operational excellence is another top goal of business process automation. Human-centric & system-centric workflow automation can improve employee & customer experience by delivering high service levels. Speed and adaptability to changing business conditions are the foremost challenges an organization faces.
Automation is the driving force that can increase operational excellence with its flexible and highly responsive solution offerings and execution. While analyzing the candidate processes, the pain points in the existing processes are often recognized, automation can resolve these challenges by simplifying the process and reducing the number the steps and finally the product cycle.
Sustainability:
Every organization should take care of future roll-outs; however, it is a daunting task. Automation techniques that take care of most business needs & processes and possess adequate opportunities to upgrade or improve the system with changing scenarios and requirements of the business environment can drive organizational sustainability. So to ensure business continuity, automation can be aimed to implement.
Quality & Cost-effectiveness:
The inclusion of automation tools and techniques is aimed to ensure consistency in terms of quality and cost-effectiveness. By eliminating human error, ensuring accuracy, and creating complex goods with fewer costs while identifying the errors along the way, it is expected automation can revolutionalize the quality control process.
Communication:
Communication is the driving force behind revenue rise and business growth. Automation can facilitate effective communication which is essential to building trust. It moves people through a funnel until the right message at each stage is delivered. One of the main goals of automation is managing communication effectively to make a decision faster. The ability to control communication goals in real-time is what makes automation an attractive investment.
Support:
The automated system is expected to handle 1:1 minor routine tasks. Also, the various business processes that are conducted in a non-functional environment are subject to uncertainty and disruption, automation creates a stable environment that supports the business processes to work efficiently.
Moreover, automation can reduce the business risks by ensuring higher regulatory compliance through granular process monitoring, error reduction, automated reporting, and auditable events trace-back.
Business Performance:
Automation transforms the business outcomes through better contract support, reduced sales cycles, increased working capital, improved customer satisfaction, and others. The innovative new solutions enabled by automation help organizations in differentiating themselves from competitors.
The manual tasks that are automated slow down the business efficiency; however, to maintain the competitive edge, agility is crucial, automation can contribute to business agility and eliminate the manual steps that are cumbersome and less effective.